
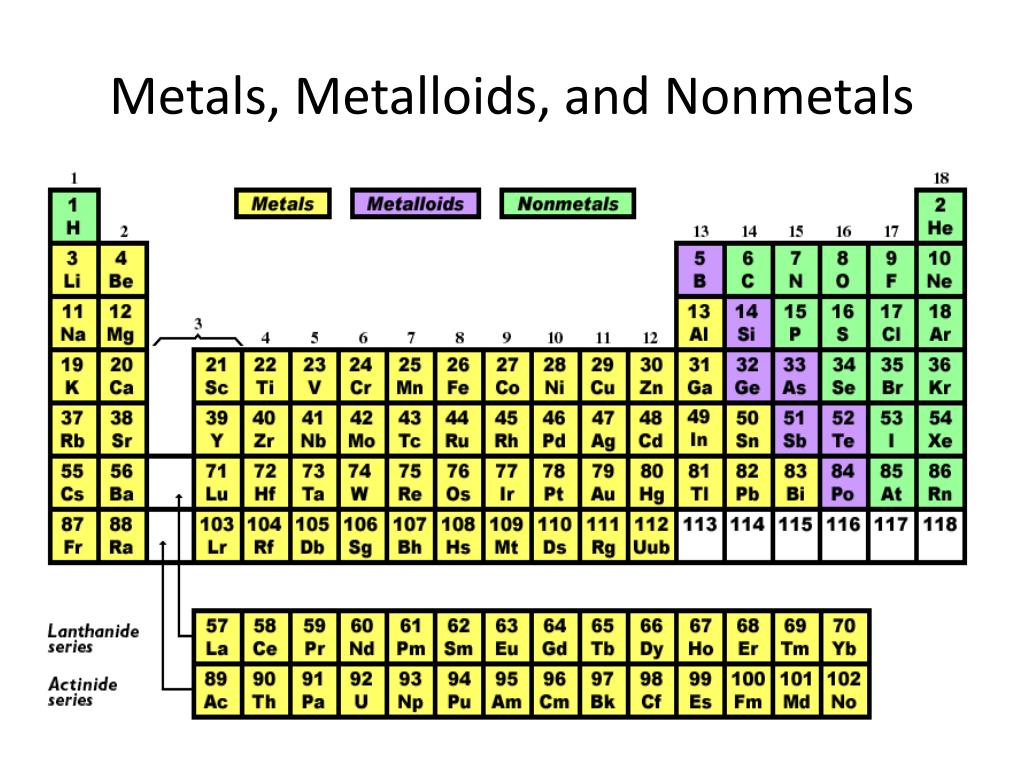
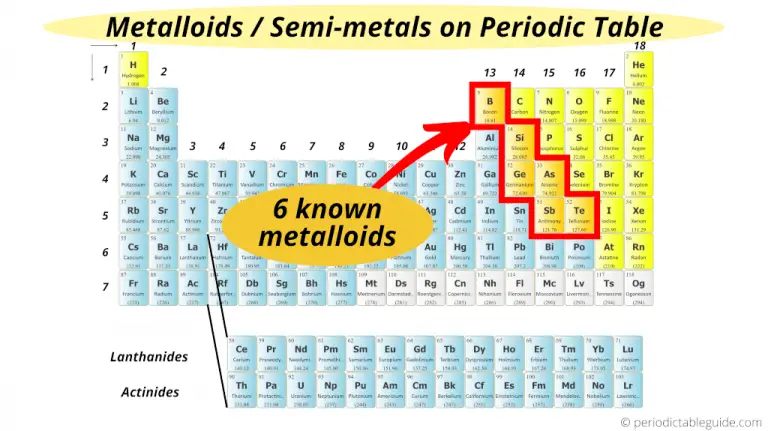
Boron is used as an alloying agent and in pesticides and insecticides. Most of the metalloids find their use in industry. These specially treated metalloids are called semiconductors. However, this phenomenon happens only when the metalloid is heated or when small amounts of certain elements are introduced in their crystal lattices (called doping). Metalloids as Semiconductorsĭue to their intermediate electronic structures, metalloids have enough empty orbitals into which electrons can move, allowing for conduction of electric current. Also, their electronegativity and ionization energies are intermediate to those of metals and non-metals. Ĭhemically, their oxides show amphoteric behavior. In addition to that, their thermal and electrical conductivities fall between metals and non-metals. Metalloids have a shiny appearance like metals but are brittle like non-metals. The difference of Metalloids from Metals and Non-metalsīy definition, metalloids show similar characteristics to both metals and non-metals. Generally, metalloids have physical and chemical properties between that of metals and non-metals.

Metallic or non-metallic behavior in chemical reactions depends upon the substance with which the metalloids are reacting.Fair conductivity at room temperature.Shiny like metals, but at the same time brittle like non-metals.Examples of Metalloids Common Properties and Characteristics of Metalloids Physical Properties


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
